What if you could send a little robot to browse the web for you? That's exactly what a bot does. web scraping : automatic data collection that interest you.

Requirements for creating a web scraping bot
To begin with, it is important to choose the right programming language for create a web scraping bot.
- Python : This is the most popular language for web scraping. It is easy to use and offers numerous libraries.
- Node.js It is ideal for managing asynchronous tasks and therefore very efficient for the scraping dynamic sites.
- Other languages For certain projects, you can also opt for the web scraping with PHP.
Once you have chosen your language, you need to select the right libraries and frameworks to simplify your scraping tasks. Here are some of the most effective:
➡ For Python:
- Requests : allows you to send HTTP requests.
- BeautifulSoup for parsing and extracting data from HTML.
- Scrapy a complete framework for more complex scraping projects.
➡ For Node.js :
- Axios Where Fetch to send HTTP requests.
- Cheerio similar to BeautifulSoup, very efficient for browsing and manipulating the DOM.
- puppeteer Where Playwright essential for scraping dynamic sites that use a lot of JavaScript.
Tutorial for creating a web scraping bot
Create a web scraping bot may seem complex. But don't worry! By following these steps, you'll have a working script in no time.
⚠ Make sure you have Python installed, along with the necessary libraries.
Step 1: Analyze the target site
Before coding, you need to know where the data is located. To do this :
-
- Open the site in your browser.
- Right-click, then select “Inspect” on the item you are interested in.
- Identify the HTML tags, classes or IDs that contain the data to be extracted (Example :
.product,.title,.price). - Test CSS selectors tags in the console (Example: if product titles are in
<h2 class="title">use this selector in your code).
Step 2: Send an HTTP request
Your bot will behave like a browser: it sends an HTTP request to the site's server, and the server returns the HTML code.
# pip install requests
import requests
url = "https://exemple.com/produits"
headers = {"User-Agent": "Mozilla/5.0"}
resp = requests.get(url, headers=headers, timeout=15)
resp.raise_for_status() # error if code != 200
html = resp.text
print(html[:500]) # previewStep 3: Parsing HTML content
Now that you've retrieved the page, you need to transform it into a manipulatable object.
It is the role of BeautifulSoup.
# pip install beautifulsoup4
from bs4 import BeautifulSoup
soup = BeautifulSoup(html, "html.parser")
products = soup.select(".product")
print(f "Products found : {len(products)}")
for p in produits[:3]:
title = p.select_one("h2.title").get_text(strip=True)
price = p.select_one(".price").get_text(strip=True)
link = p.select_one("a")["href"]
print({"title": title, "price": price, "link": link})Step 4: Extract data
This is the most interesting step: finding specific information such as titles, prices, and links.
from urllib.parse import urljoin
base_url = "https://exemple.com"
data = []
for p in soup.select(".product"):
title = p.select_one("h2.title").get_text(strip=True)
prix_txt = p.select_one(".price").get_text(strip=True)
lien_rel = p.select_one("a")["href"]
lien_abs = urljoin(base_url, lien_rel)
# normalization price
price = float(price_txt.replace("€","").replace(",",".").strip())
data.append({"title": title, "price": price, "url": link_abs})
print(data[:5])Step 5: Back up data
To avoid losing your results, you can save them in the CSV Where JSON.
import csv, json, pathlib
pathlib.Path("export").mkdir(exist_ok=True)
# CSV
with open("export/produits.csv", "w", newline="", encoding="utf-8") as f:
fields = ["title", "price", "url"]
writer = csv.DictWriter(f, fieldnames=champs, delimiter=";")
writer.writeheader()
writer.writerows(data)
# JSON
with open("export/products.json", "w", encoding="utf-8") as f:
json.dump(data, f, ensure_ascii=False, indent=2)
print("Export complete!")How to circumvent web scraping protection measures?
It's important to know that sites use a number of mechanisms to protect their data. Understanding these protections is essential to scrapping efficiently and responsibly.
- robots.txt
📌The robots.txt file indicates which pages a bot can or cannot visit.
✅ Always check this file before scraping a website. Complying with it will help you avoid unauthorized actions and legal issues.
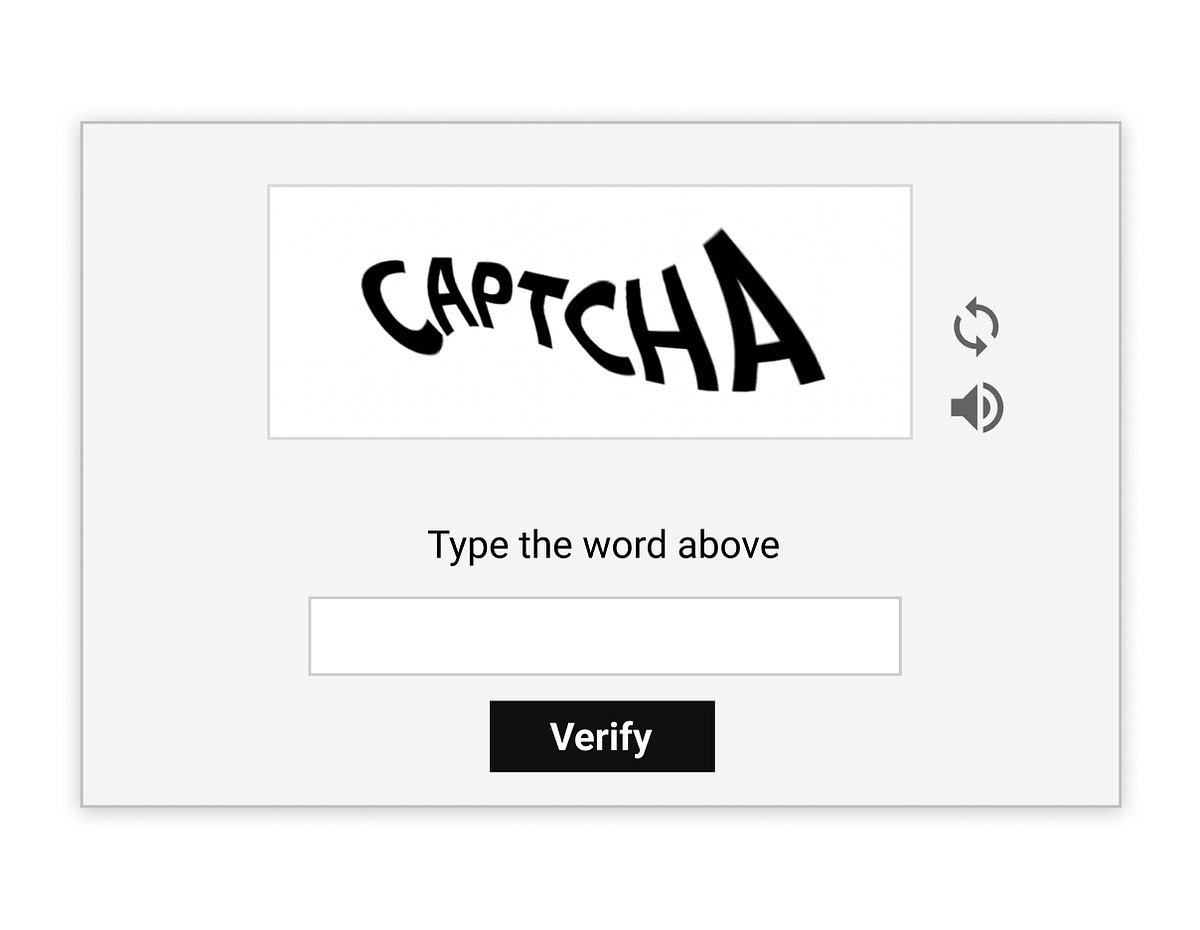
- Captchas
📌 They are used to verify that the user is human.
✅ To bypass them, use automation libraries to simulate a real browser or third-party services specializing in solving captchas.
- Blocking by IP address
📌 Some websites detect a large number of requests coming from the same IP address and block access.
✅ It is therefore recommended to use proxies or a VPN to change your IP address regularly.
- User-agent blocks
📌 Sites can refuse requests from bots identified by suspicious User-Agent.
✅ The trick is to define a realistic User-Agent in your HTTP requests to simulate a conventional browser.
- JavaScript websites
📌 Some pages load their content via JavaScript, preventing simple HTTP requests from retrieving the data.
✅ To get around them, you can use tools like Selenium, Playwright or Puppeteer.
FAQs
What's the difference between a web scraping bot and a web crawler?
| Web scraping | Web crawler |
|---|---|
| Focuses on specific data titles, prices, product links, etc. The bot reads the HTML, identifies the relevant elements and extracts them for further use (analysis, storage, export, etc.). |
It is a program that automatically browses web pages by following links in order to discover content. Its main purpose is to crawl the web to map and index information, but not necessarily to extract specific data. |
Is web scraping legal?
The legality of web scraping varies depending on the website, the type of data collected, and how it is used.
What types of data can be extracted with a web scraping bot?
With a web scraping bot, you can collect :
- 🔥 Des titles and descriptions products.
- 🔥 Des prices and promotions.
- 🔥 Des internal or external links.
- 🔥 Des user reviews and ratings.
- 🔥 Des contact information.
- 🔥 Des textual content or images web pages.
How can a website detect my scraping bot?
Sites often detect bots through abnormal behavior such as :
- ❌ the query speed too high or regular
- ❌ the’non-standard user-agent
- ❌ the’no loading of JavaScript resources required
- ❌ the cookie-free browsing, etc.
What are the common challenges when creating a web scraping bot?
Creating an effective bot is not always easy. Common challenges include:
- 🎯 them inconsistent HTML structures.
- 🎯 them unstructured data.
- 🎯 them slow loading problems pages.
Are there any web scraping services or APIs?
Yes ! There are services that simplify scraping and manage aspects such as proxies, captchas and dynamic sites.
You can also use Web scraping API to access structured data. Bright Data is one of the most comprehensive solutions.
💬 In short, web scraping opens up many possibilities for exploiting web data. Creating a web scraping bot allows you to automate data collection.




